Transactions in the Bitcoin Network
Put yourself in the position of making a transaction of bitcoins for any good you want to buy. Did you ever wonder how the transactions is taken, where it goes, and how is it confirmed. In this article we will present how transactions in the bitcoin network works.
How a Bitcoin Transaction is made Let us say that your closest grocery store accepts Bitcoin as payment. In order to pay with your own bitcoin you will need a wallet. The wallet is an application that stores information securely in a database or a file.
That wallet contains information about your Bitcoin client like digital signatures, digital keys and your bitcoin address.
All transactions will require your bitcoin address. Eventually the customer will have to scan a QR Scan which can be either the shop’s bitcoin address or an URL-encoded Payment Request that prefills the information for the payment.
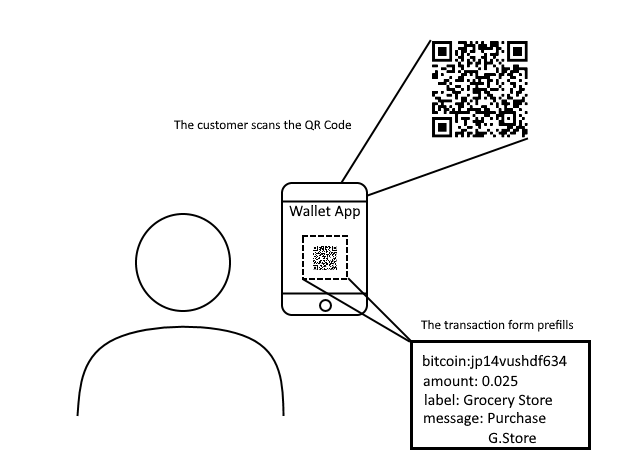
Bitcoin Transaction Propagation
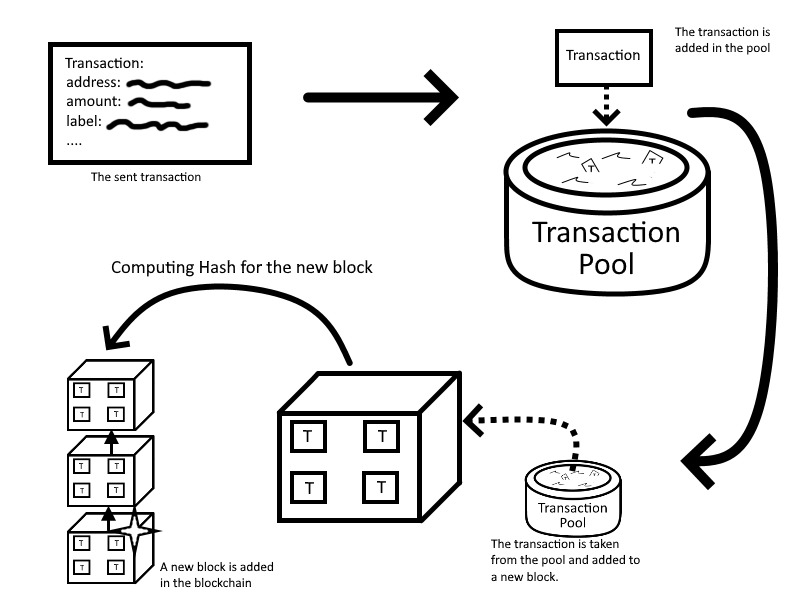
Now that the transaction was sent we will look into how the transaction propagates in the Bitcoin Network. The transaction is set but not verified. So in order to be verified it has to be included in the Blockchain (distributed ledger). Once you send the transaction it is put into a temporary pool where from there is getting into a block. Miners get those transactions from the pool and mine the next hash for the block. Once the next hash has been found the block is created with the transactions from the pool. Now the transaction is verified.
Advantages
- You will not have to carry your currency all around so you will have your money on your phone.
- Moreover since it is Bitcoin there is no central authority to validate your transactions.
- Besides, It is blockchain so it would be faster for your bitcoin transactions to validate (10 minutes for a new block) than online bank transactions that would take up to 24 hours to validate or whenever the bank works.
